Understanding Scabies and Its Impact
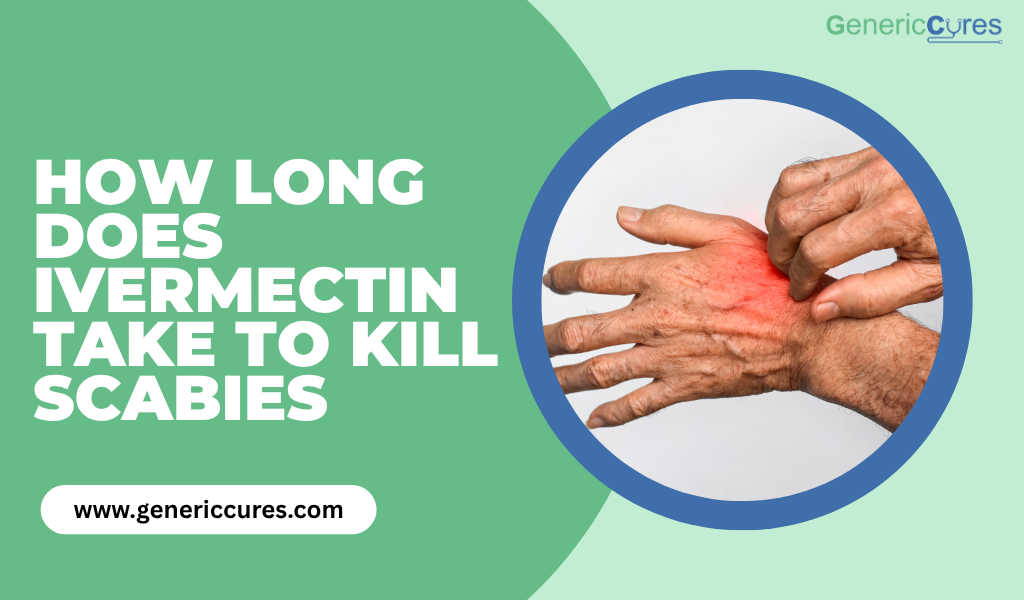
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These microscopic parasites burrow into the skin, lay eggs, and cause intense itching, inflammation, and rashes. Scabies can affect anyone—regardless of age, hygiene, or lifestyle.
What Is Scabies?
Scabies spreads rapidly through close physical contact and shared items like towels or bedding. It manifests as:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Red, bumpy rashes or blisters
- Thin, irregular burrow tracks on the skin
The infestation often appears in warm, folded areas like the fingers, waistline, armpits, and groin.
What Is Ivermectin?
Ivermectin for Humans is an oral antiparasitic medication approved for treating several parasitic infections, including scabies. It works by disrupting the nervous system of mites, paralyzing and killing them.
Ivermectin is commonly prescribed when:
- The infestation is widespread
- Topical treatments fail
- Crusted scabies is present
- Treating multiple individuals in an outbreak
How Long Does Ivermectin Take to Kill Scabies?
Within 24 to 48 Hours for Adult Mites
After ingestion, Ivermectin begins to work in about 24–48 hours, effectively killing most adult mites. However, it does not kill the eggs, which means newly hatched mites can survive unless a second dose is taken.
Second Dose After 7–14 Days
To completely eradicate the infestation, a second dose is typically administered 1 to 2 weeks later. This ensures that any newly hatched mites are also killed before they can reproduce.
What Is Iverjohn 12?
Iverjohn 12 is a commonly prescribed Ivermectin medication available in 12 mg dosage, ideal for adult scabies treatment. It is known for:
- Quick action
- High effectiveness
- Suitability for systemic infestations
One tablet is often enough for mild cases, but more severe infestations may require repeat dosing based on body weight and medical guidance.
Why Does Itching Continue After Treatment?
Many patients expect immediate relief, but itching can persist for several weeks even after successful treatment. This is due to:
- Allergic reactions to dead mites and their waste
- Skin inflammation from scratching
- Residual effects of burrowing
This condition is called post-scabies itch and usually resolves in 2–4 weeks. Use antihistamines, steroid creams, or moisturizers to soothe symptoms during recovery.
Using Ivrea Cream: A Topical Complement
Ivrea cream, a topical Ivermectin formulation, is an excellent addition to oral treatment, especially for localized infestations or patients who cannot take oral meds. It:
- Kills mites on contact
- Is easy to apply from neck to feet
- Typically needs one or two applications
Applied correctly, Ivrea cream can drastically reduce mite population and speed up skin recovery.
How to Maximize Treatment Success
For the fastest and most effective scabies treatment, follow these steps:
1. Hygiene and Cleaning
- Wash all bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water
- Dry items on high heat or store in sealed plastic for 72 hours
- Vacuum mattresses, couches, and carpets
2. Treat Close Contacts
Everyone in your household or intimate circle should be treated at the same time, even if asymptomatic.
3. Follow Dosage Instructions
Always take Iverjohn 12 or any Ivermectin exactly as prescribed. A second dose is essential for full eradication.
Precautions While Taking Ivermectin
While Ivermectin for Humans is generally well-tolerated, it may cause mild side effects such as:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Mild skin reactions
Seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, rash, or swelling.
When to See a Doctor
Consult your healthcare provider if:
- Itching lasts more than 6 weeks
- New burrows or rashes appear after treatment
- You develop secondary infections (e.g., from scratching)
Sometimes, additional treatments or alternative medications may be required.
Scabies in Special Populations
Children and Infants
Topical creams are generally preferred. Consult a pediatrician before using oral medications.
Elderly or Immunocompromised
They are at higher risk for crusted scabies and may require more aggressive treatment, including a combination of Ivrea cream and oral Ivermectin.
Natural Remedies – Do They Help?
Some people try tea tree oil, neem, or turmeric as natural remedies. While they may help reduce inflammation, they are not substitutes for medical treatment. Scabies requires approved antiparasitic medications for complete eradication.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- Ivermectin kills adult scabies mites within 24–48 hours, but not the eggs
- A second dose is critical after 7–14 days to prevent reinfection
- Ivrea cream can enhance treatment, especially for localized or topical application
- Itching may persist for up to 4 weeks after successful treatment
- Always treat everyone in close contact and clean household items thoroughly
- For trusted treatment, visit Genericcures
Final Words: Relief Is Within Reach
Scabies can be emotionally and physically exhausting, but with proper medication like Iverjohn 12 and effective hygiene practices, full recovery is possible. Understanding the treatment timeline helps set realistic expectations and avoids unnecessary worry.
If you’re struggling with persistent symptoms, talk to a healthcare professional. Early and effective treatment ensures a fast return to comfort and peace of mind.
Visit here for more – Does Ivermectin Kill Scabies Immediately